Trading Options Premiums And Using The Greeks
I’m Meta Matt, Director of Education and welcome to PB University LITE! This is a 50 Class Trading 101 Series geared towards both new and veteran traders alike! We go over everything from Trading Psychology, Technical Analysis, and Options Trading to Commodity Trading, Forex, and more!! This 50 Class series is not designed be taken in order, it is instead designed for traders to browse and pick which classes interest them. I will include the list of classes at the bottom of this page.
Start Trading With Webull: Free Stock Shares
Custom Trading Indicator DISCOUNT: Try StocksBuddy Today
Get A Trading Coach, Premium Alerts, Education, and Community:
1 Month Membership
90 Days (Save 10% Per Month)
1 Year (Save $279)
So there are ways to make, or lose money before the expiration date. You do this by trading the premium. In order to understand that we need to dive into The Greeks.
The Greeks are a set of metrics that options traders use to understand the risk and potential rewards of their positions.
Simply speaking, the Greeks help us determine what the Option is truly worth, and how much it can appreciate or depreciate based on certain factors such as time, price movement, and volatility.
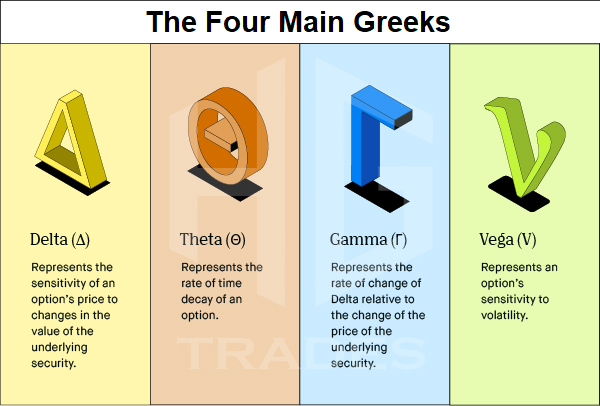
DELTA
Delta measures the sensitivity of an option's premium to the price of the stock, so basically it shows how much the premium will move if the stock price moves $1.
A delta of 0.50 means that for every $1 move in the stock, the option premium will move by $0.50. It will go up that much if the stock goes up and down if the stock goes down…
So if the Delta is .3, that means the premium or price of the option will go up $0.30 if the stock goes up $1, or down $.30 if the stock was to go down $1. Delta ranges from 0 to 1 for CALL options and -1 to 0 for PUT options.
GAMMA
Gamma measures the rate of change of the delta. It tells us how much the delta of an option will change for every $1 move in the stock.
So when the stock price changes, the premium changes based on the delta, and the delta of the option changes as well, the gamma is what tells us how much the delta is changing.
For example, if a call option has a delta of 0.5 and a gamma of 0.05, that means that if the stock price goes up by $1, the delta of the option will increase by 0.05, so the delta of the option will become 0.55. In general, options with a high gamma will have a more rapid change in delta as the stock price changes, while options with a low gamma will have a slower change in delta. Meaning that the premium aka price of the option will most likely move slower as well.
THETA
Theta measures the rate at which an option's value erodes over time.
Meaning It tells you how much an option will lose in value each day as expiration approaches (assuming there is no change in the stock price).
A high theta means that the option is losing value rapidly.
VEGA
Vega measures the sensitivity of an option's price to changes in implied volatility. Implied volatility is a measure of the market's expectations for how much the underlying asset will move, or fluctuate in the future.
Volatility is when a stock goes up or down quickly, so Implied volatility is the market's measure of whether or not the stock in question will be volatile or not.
In general, a high vega option is more sensitive to changes in implied volatility, meaning that if implied volatility goes up, the option price is likely to go up as well. Conversely, if implied volatility goes down, the option price is likely to go down as well.
RHO
Rho measures the sensitivity of an option's price to changes in interest rates.
In general, options on stocks with far out expiration dates are more sensitive to changes in interest rates, and therefore have a higher rho, compared to options with shorter expiration dates.
A positive rho means that an increase in interest rates is expected to lead to an increase in the option's price, while a negative rho means that an increase in interest rates is expected to lead to a decrease in the option's price. Rho is usually only important for options that are not close to expiration.
So let’s say that it’s January 1st, and I buy a CALL for stock $XYZ with a $30 Strike Price, February 3rd Expiration, and $.50 Premium.
So this option CALL will cost me $50. Now let’s say that the price of the stock is $30 when I buy the CALL, but a week later, it goes to $33, and based on that Options Greeks, remember the delta shows us how much the premium goes up every time the stock goes up $1, and in this example the stock has gone up $3. So let’s say that the premium is now no longer $.50, but is now $1.50.. Meaning my Options Contract that I bought for $50, is now worth $150. So that’s a $100 profit if I sell the contract.
A lot of people prefer to trade the premiums this way, especially if they don’t have the capital to actually buy the 100 shares at $30 if they were to execute the contract.
You can buy CALLS and PUTS, but you can also short Sell CALLS and PUTS. Tune into Class #13 where we talk all about it!!

PB University LITE Class List
1) Trading Terminology
2) Stock Market Indices
3) Common, Preferred, and Penny Stocks
4) Diversification of Assets
5) Fundamental Analysis Made Easy
6) Technical Analysis Made Easy
7) Risk Management In The Market
8) Portfolio Management
9) How To Follow Market News
10) Trading Psychology
11) Options Explained
12) The Greeks In Options Trading
13) How To Short Sell Options
14) Covered CALLS
15) Spread Trading
16) Online Brokers for Options Trading
17) Implied Volatility Calculators & Tools
18) Protective PUTS
19) Iron Condors
20) Straddles
21) Reading Level 2
22) Taxes
23) Trading Psychology Techniques
24) The Art Of Trading
25) Becoming A Jedi In The Stock Market
26) Futures Trading Explained
27) Commodity Trading 101
28) Regulatory Environments
29) How To Become A Millionaire
30) $100K In 100 Days
31) Wash Sale Rule
32) Behavioral Finance Part 1
33) Behavioral Finance Part 2
34) 5 Charting Indicators
35) Fair Value Gap
36) Insider Trading and Market Manipulation
37) Stock Chart Types
38) Moving Averages 101
39) Base vs Precious Metals
40) Electricity Trading 101
41) Trading Brokers 101
42) 5 Trading Strategies
43) 85% Trading Rule
44) Are Win Rates A Scam?
45) Futures Trading 101
46) ATR Indicator Strategy With The Greeks
47) MACD Indicator 101
48) Bollinger Bands Indicator 101
49) Wedges, Triangles, Flags and Pennants
50) RSI Divergence 101